When cycling, your leg and trunk (core) muscles are the main muscles involved. But your arms are also working as you climb or ride out of the saddle.
Limbs
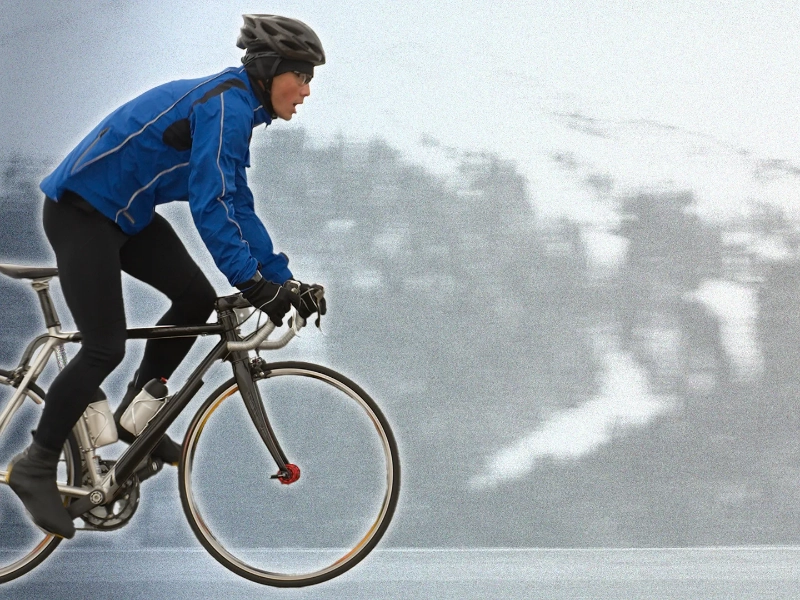

The quadriceps are the main muscle group that is used when riding. However, cycling also tones and strengthens the muscles in the hamstrings, calves, and glutes.
Riding a bike will burn calories, which will aid in body fat loss and the development of a leaner physique. Cycling can burn up to 260 calories in an hour, depending on your speed.
Try to pedal a full revolution with each stroke to get the most out of your leg workout. According to Schwartz, doing this will equally train your legs' front and back sides. You can increase the difficulty by adding pushing or climbing, as these exercises target your quadriceps even more.
Remember that while cycling can help you tone your muscles, it won't help you gain huge muscles like weightlifting can. Combine weight-training exercises like squats with cycling to witness considerable muscle growth.
Central
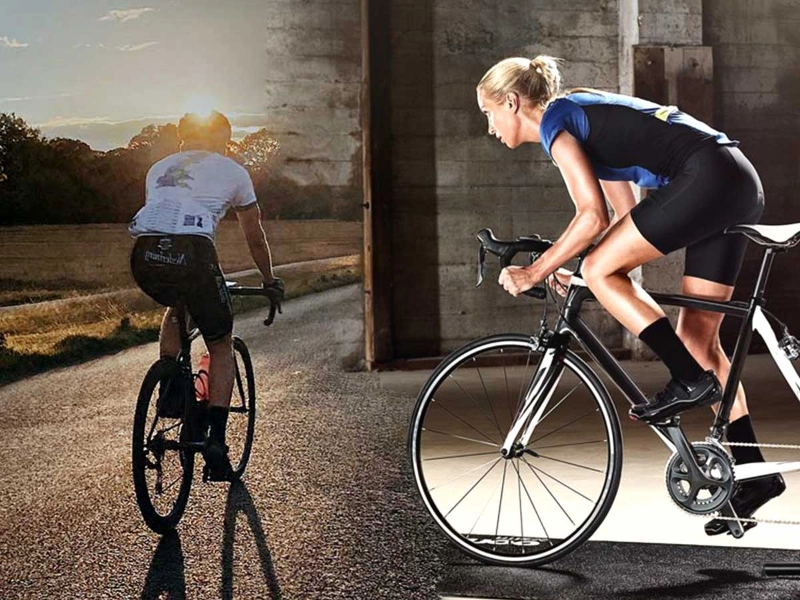

Bike riding can help, whether your goal is to tone up that area or slim down your butt. It's a fantastic choice since it helps you gain muscle without gaining bulk and burn calories.
Cycling works your core muscles, which creates a solid foundation for generating power and maintaining balance. Together, the rectus abdominis and erector spinae, two abdominal muscles, help you maintain your body's stability on the saddle and effectively transfer power with each pedal stroke.
Maintaining proper posture on the bike, as opposed to slouching or hunching over, will also help you tone your abs. Simple core workouts like hovering or taking one hand off the handlebars for a brief period of time can even be performed while riding. This strengthens your abs and improves the efficiency of your muscular contractions. This might lessen the likelihood of swaying or rocking, which can cause saddle sores and lower back pain. This position can improve your mood and confidence, in addition to making riding more efficient.
Weapons
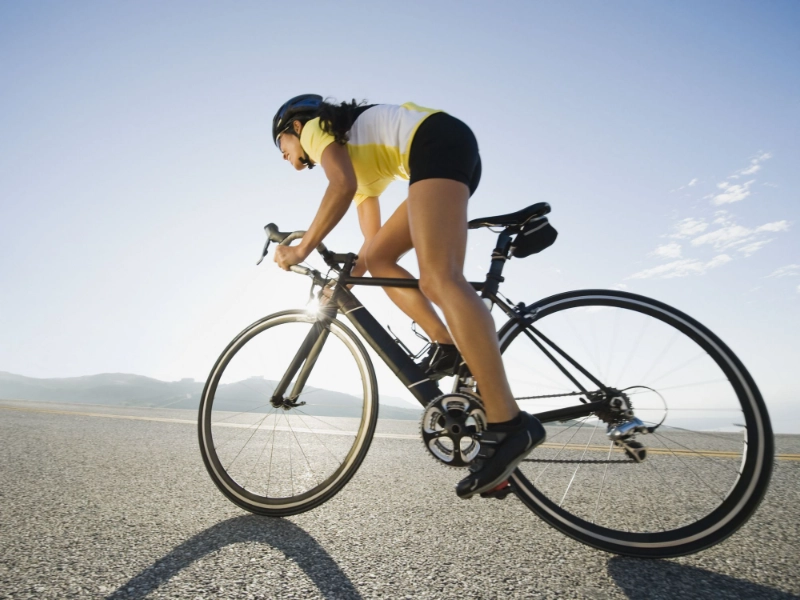

Even though the legs are generating most of the force, the arms are working very hard as well. While riding, your triceps, biceps, and deltoids are used to keep your body upright, which tones and strengthens your arms.
Depending on the surface you're riding on, the muscles you use to cycle can vary. For instance, Sebastian explains that climbing a hill uses more quad and calf muscles than moving across level terrain. In addition, you will use your upper body muscles to help balance your body weight on the pedals if you ride your bike quickly.
Additionally, cycling increases metabolism and heart rate, which helps reduce the risk of high blood pressure and heart disease. Including bicycling in your daily routine can also help you feel happier and less stressed, as well as minimize the amount of time you spend in your automobile and lessen your carbon footprint. Just be sure to invest in comfortable bottoms that won't rub against the saddle when purchasing a pair of bike shoes that fit well. Qayed continues.
Upper torso
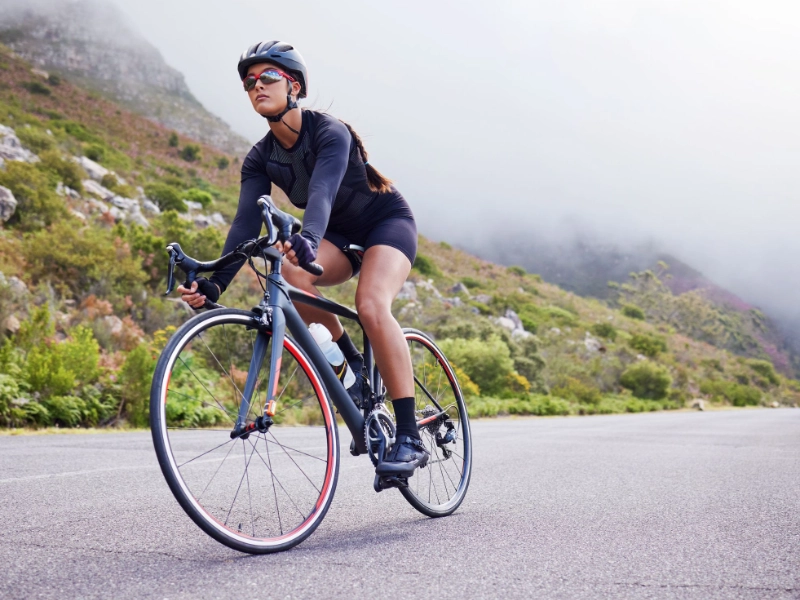

While cycling, the leg muscles are the main force behind the movement; however, the arms and core also play a role. As you pedal on the bike, your biceps, triceps, shoulders, and chest work to stabilize your body.
The surface you ride on outside will also affect how hard your upper body needs to work. While riding up a hill requires more strength from your quads and calf muscles, riding downhill primarily relies on momentum rather than leg strength.
When it comes to cardiovascular exercises, riding is a pretty easy exercise that works well for virtually everyone. It doesn't necessarily tone your muscles, though; you still need to combine biking with other strength-training activities if you want to gain muscular mass. Having said that, your painful butt will probably come to appreciate the workout if you persevere. Additionally, you'll be benefiting your immune system in the process.
Advertisement
Recommended Reading: Why is climbing mountains a sport?























Comments
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *